F-doped cesium tungsten bronze may be used for producing heat insulating window glass with high energy efficiency. But what is the change of F doping cesium tungsten bronze when it is heat treated in the rising temperature? We can look at the SEM images of F-doped cesium tungsten bronze annealed at different temperature for 30min under N2 atmosphere. Wherein, (a) is not heat treated; (b) is heat treated at 400°C; (c) is heat treated at 500°C; (d) is heat treated at 600°C; and the amount of HF added is 0.45.
More details, please visit:
http://cesium-tungsten-bronze.com/index.html
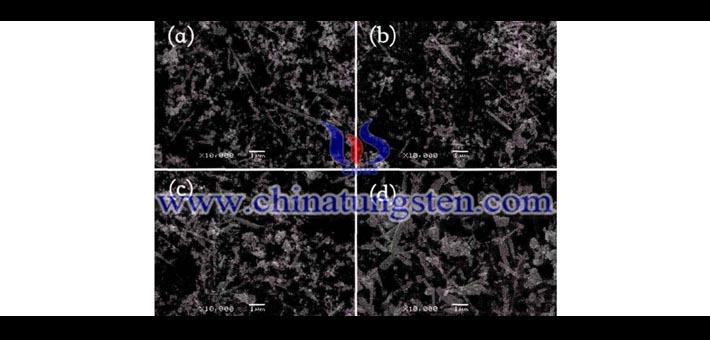
From the above image, we can see that the morphology of the F-doped cesium tungsten bronze crystal becomes thicker as the heat treatment temperature increases. Meanwhile, the aspect ratio is compressed. The morphology of the unheated F doping cesium tungsten bronze is mainly distributed in form of needle crystals. After heat treatment at 400°C, some of the needle crystals become coarse, and the crystals after heat treatment at 500°C are mainly rod-shaped, and the crystals after heat treatment at 600°C become short and thick. Since a large aspect ratio is advantageous for absorbing near-infrared rays, the absorption ability of F-doping cesium tungsten bronze with short and thick morphology caused by heat treatment to near-infrared rays may be reduced.




