PART IV OUTSTANDING PROBLEMS & SOLUTIONS OF CHINA TUNGSTEN
4.1 Outstanding Problems Faced
4.1.1 Consumption Rate of Tungsten in China is Higher than the Global Average
China's tungsten resources account for less than 60% of the global reserves, but the exploitation volume has reached more than 80% of the world. The resource consumption rate of China is higher than the global average, and the resource advantage is gradually weakening. Although the identified tungsten resource reserves have increased, the updated basic reserves have decreased significantly, and the newly discovered large-scale mineral resource endowment is relatively poor. Under the current technical conditions, the economic benefits of development and utilization are expected to be poor.

The good comprehensive performance of tungsten cemented carbide tools makes them widely used in the processing of steel, stainless steel, cast iron, non-ferrous metals, heat-resistant steel and hardened steel materials, accounting for about 63% in the global tool market and 53% in the China. Cutting accounts for about 90% of the whole machining workload, efficient and advanced cutting tools can significantly improve the machining efficiency and reduce the production cost by 10% ~ 15%. Cutting tool materials should have the characteristics of hardness and wear resistance, strength and toughness and heat resistance. Cutting tools mainly include cemented carbide, high-speed steel, ceramics and super hard materials; Among them, cemented carbide has higher hardness, wear resistance and red hardness compared with high-speed steel, and cemented carbide has higher toughness compared with ceramics and super hard materials.
4.1.2 The Production Capacity of High-end Tungsten Products Needs to be Improved.
In recent years, China has developed rapidly in tungsten deep processing, and has made great achievements in Numerical Control (NC) blade, PCB micro drill and high-performance tungsten materials. However, at present, more than 10 billion RMB Yuan of high-end tungsten products are still imported from abroad every year; The price of imported tools is much higher than the export price. The average import price of coated blades is about 3.81 times that of export, 6.41 times that of uncoated blades, 2.71 times that of milling cutters and 17.06 times that of measuring tools. Domestic product upgrading has a long march to go, and localization still has great potential. 60% of the exported tungsten products are raw material grade tungsten products. In terms of industrial structure, the proportion of deep processing is relatively small, and its global advantages are still concentrated in the upper reaches of the industrial chain; The market share of high-end tungsten products is still relatively low, and the overall solution service system is in its infancy
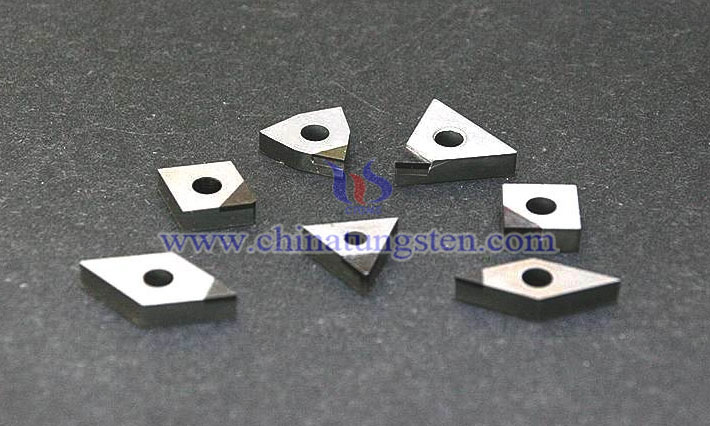

Tungsten cemented carbide numerical control (NC) blade
4.1.3 China's Capacity of High-end Equipment for Tungsten is not Enough
The machining accuracy of China's cutting tool products is close to the international advanced level, and the matching of key equipment is one of the important links. There is still a certain gap between China's key equipment and the international leading level, and some high-end equipment for tungsten manufacturing depends on imports.
4.1.4 The Market Mechanism is Single and Lack of Innovation and Vitality
The concentration of China's tungsten industry is relatively low, and the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain are in a full competition pattern. Under the single spot market mechanism, the market competition consumes technological progress and resource advantage dividends. The overall benefit level of the industry is relatively low, which restricts the R & D investment and industrial upgrading process, and the value of strategic metals has not been fully reflected.

Powder metallurgy pressure sintering furnace, Made in China. In order to promote the implementation of “China's tungsten industry development plan (2021-2025)”, understand the gap between the current situation of tungsten industry equipment and foreign advanced equipment and the development ideas of key equipment in the future, build an exchange platform for equipment manufacturing, technology and application, and promote coordinated development, CTIA plans to hold the "China Tungsten Industry Equipment Industry Forum" (hereinafter referred to as the CTEIF) in September in Xiamen, China every two years. CTEIF will be Supported by Xiamen Tungsten Industry Co., Ltd. and China Tungsten High Tech Materials Co., Ltd., CTEIF will be hosted by geological and Mining Branch, Smelting Branch Tungsten C Cemented Carbide Branch, Tungsten Raw Material Branch, Tungsten Ferro Alloy Branch of CTIA and China Tungsten Online. CTEIF plans to hold 12 thematic reports on advanced equipment and technology in tungsten industry, and the conference will collect and publish the list of tungsten industry equipment, tools, analysis and testing instruments. In particular, the meeting welcomes the active participation of all international manufacturing and processing equipment, inspection and testing manufacturers, intelligent manufacturing software and hardware manufacturers and service providers for tungsten, molybdenum and rare earth mining, smelting and production. For details, please contact Miss Zheng, Secretary of the Permanent Management Office of the CTIAIF [email protected] , or please visit CTIA’s web, also, please follow us at about CTEIF here belew.
4.2 Suggestions for China's Tungsten Industry
4.2.1 Slow Down the Consumption of Tungsten Resources
Great attention should be paid to slowing down the rate of resource consumption, maintaining the sustainable and healthy development of the industry and improving the ability of strategic resource support. Reducing the rate of resource consumption to the global average and matching the resource reserves is a phased goal. The specific measures are as follows: first, continue to implement and optimize the management policy of total tungsten mining index control, and orderly develop and utilize tungsten resources on the premise of fully ensuring the development of national economy; Second, accelerate the pace of "going global", coordinate the international and domestic markets and resources, actively carry out international cooperation, and encourage backbone enterprises with strong international operation ability to explore and exploit overseas resources; The third is to increase the recycling of waste tungsten and moderately liberalize the import of qualified renewable raw materials of tungsten resources; the fourth is to strengthen the deep edge prospecting of mines in production and prolong the service life of mines.
4.2.2 Continue to Promote & Upgrading the High-quality Development of Tungsten Industry

The vitality and hope of China's tungsten industry not only come from our rich tungsten resources, but also from the long-term unremitting technical research and improvement of production capacity with China's tungsten products enterprises.
Introduce special incentive policies to encourage the tungsten industry to take scientific and technological innovation as the driving force, improve industrial profitability, improve industrial structure, enhance international competitiveness and promote the high-quality development of the tungsten industry. (1) Improve the innovation system of tungsten industry, focus on intensive processing technology, aim at the scientific and technological frontier of the development of tungsten industry, strengthen basic research and lead major breakthroughs in original achievements; (2) Expand the application of tungsten terminals, focus on the research and development of tungsten precision and deep-processing products, strengthen the research on common technologies, and expand the application of tungsten in various fields of the national economy; (3) Promote the intelligent manufacturing of high-end cemented carbide and support the technological progress of key equipment; (4) Governments at all levels should increase their support, support enterprises' scientific and technological investment, talent introduction and training, and reward original core technological achievements; (5) Promote the supply side reform of the tungsten industry, improve the industry access system, study and formulate supporting regulatory measures, stop low-level repeated construction, promote energy conservation and emission reduction, prevent pollution, and eliminate production lines with backward technology and unqualified safety and environmental protection.
4.2.3 Improve the Management Policy of Tungsten Industry.
From the perspective of strategic resources, re-examine the management policy of tungsten industry, and build and improve the strategic resource management policy system. Improve the development and management mechanism of tungsten resources, regulate the "main gate" of tungsten resource allocation, and promote the protection and rational development and utilization of tungsten resources; Implement the dynamic strategic reserve mechanism to maintain the healthy operation of the industry and ensure the autonomy and controllability of key industrial chains; Optimize and implement policies related to renewable resources and raise renewable utilization to the height of industrial strategy.
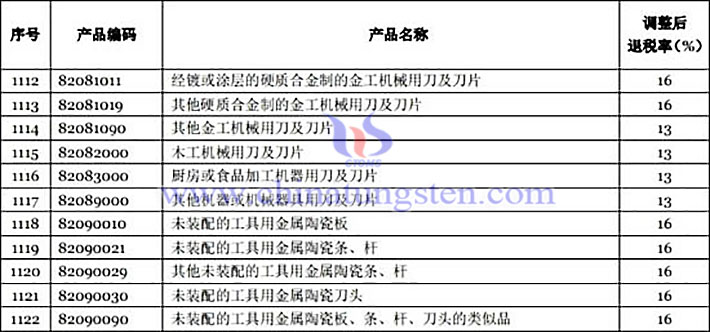
Since November 1, 2018, China has increased the export tax rebate rate of some tungsten cemented carbide blades and other cutting, drilling and other tools to 16%. For products not involved in the table, if the original export tax rebate rate is 15%, the export tax rebate rate will be increased to 16%; If the original export tax rebate rate is 9%, the export tax rebate rate will be increased to 10%; If the original export tax rebate rate is 5%, the export tax rebate rate will be increased to 6%. This policy is a favorable policy for the development of China's cemented carbide industry, especially high-end CNC cutting tools.
Since November 1, 2018, China has increased the export tax rebate rate of some tungsten cemented carbide blades and other cutting, drilling and other tools to 16%. For products not involved in the table, if the original export tax rebate rate is 15%, the export tax rebate rate will be increased to 16%; If the original export tax rebate rate is 9%, the export tax rebate rate will be increased to 10%; If the original export tax rebate rate is 5%, the export tax rebate rate will be increased to 6%. This policy is a favorable policy for the development of China's cemented carbide industry, especially high-end CNC cutting tools.
4.2.4 Improve the Market Mechanism and Enrich the Market Regulation Tools.
Research on listed tungsten futures, enrich the market mechanism, provide hedging tools for the industry, enable the financial attribute of tungsten strategic resources, help the scientific and technological innovation of the industry, and promote the sustained, healthy and high-quality development of the industry
Any more about China Tungsten, and any news about tungsten worldwide, please visit CTIA, Any questions, comments and suggestions, please contact: [email protected].
Tungsten Cemented Carbide Coated Cutting tools, NC blades will be the technical direction that China Tungsten Industry, especially tungsten cemented carbide enterprises will strive to improve for a long time in the future.

Physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a method of producing hard coatings on metal substrates. It generates locally ionized metal vapor, reacts with specific gases, and forms thin films with specified components on the substrate. The most common methods are sputtering and cathodic arc. In sputtering, steam is generated by bombarding metal targets with energetic gas ions. The cathode arc method uses repeated vacuum arc discharge to impact metal targets and evaporate materials. All PVD processes are carried out under high vacuum. PVD process is used for the coating of a large number of tools and components. The coating is composed of nitrides, carbides and carbon nitrides and alloys of Ti, Cr and Zr, such as alcr, alti and TiSi. Applications include cutting and forming tools, mechanical components, medical devices and products that benefit from the hard and decorative characteristics of coatings. Typical process temperatures for PVD coatings are between 250 and 450 ° C. In some cases, PVD coatings can be deposited at temperatures below 70 ° C or up to 600 ° C, depending on the substrate in the application and the expected performance. The coating can be deposited in single, multiple and graded layers. The latest generation of thin films are multilayer coatings with nanostructure and superlattice changes, which provide enhanced properties. The coating structure can be adjusted according to hardness, adhesion and friction to produce the desired performance. The final choice of coating depends on the requirements of application. The coating thickness ranges from 2 to 5 microns, but can also be as thin as hundreds of nanometers or as thick as 15 microns or more. Base materials include steel, non-ferrous metals, tungsten carbide and pre–Electroplated Plastics. The suitability of PVD coating substrate is only limited by its stability in terms of deposition temperature and conductivity.
Physical vapor deposition (PVD) is a method of producing hard coatings on metal substrates. It generates locally ionized metal vapor, reacts with specific gases, and forms thin films with specified components on the substrate. The most common methods are sputtering and cathodic arc. In sputtering, steam is generated by bombarding metal targets with energetic gas ions. The cathode arc method uses repeated vacuum arc discharge to impact metal targets and evaporate materials. All PVD processes are carried out under high vacuum. PVD process is used for the coating of a large number of tools and components. The coating is composed of nitrides, carbides and carbon nitrides and alloys of Ti, Cr and Zr, such as alcr, alti and TiSi. Applications include cutting and forming tools, mechanical components, medical devices and products that benefit from the hard and decorative characteristics of coatings. Typical process temperatures for PVD coatings are between 250 and 450 ° C. In some cases, PVD coatings can be deposited at temperatures below 70 ° C or up to 600 ° C, depending on the substrate in the application and the expected performance. The coating can be deposited in single, multiple and graded layers. The latest generation of thin films are multilayer coatings with nanostructure and superlattice changes, which provide enhanced properties. The coating structure can be adjusted according to hardness, adhesion and friction to produce the desired performance. The final choice of coating depends on the requirements of application. The coating thickness ranges from 2 to 5 microns, but can also be as thin as hundreds of nanometers or as thick as 15 microns or more. Base materials include steel, non-ferrous metals, tungsten carbide and pre–Electroplated Plastics. The suitability of PVD coating substrate is only limited by its stability in terms of deposition temperature and conductivity.
Read/download the full report:



